Mitsui's Forests
About Mitsui's Forests
Mitsui & Co. owns forests in 74 locations in Japan, from Hokkaido in the north to Kyushu in the south. Mitsui's Forests cover a total area of approximately 44,000 hectares, which is equivalent to about 70% of the area of Tokyo's 23 wards, or 0.1% of Japan. Mitsui stably provides timber that accounts for about 0.1% (approximately 40,000 m3) of the annual demand for timber in Japan
Forest Management Approach
The principle that underpins all our forest management efforts is to realize sustainable forests by practicing appropriate forest management and operations that will protect and nurture each forest's various functions. We own a vast area of forest and to fulfill our social responsibilities as the steward of these precious natural resources, we manage them as sustainable forests, including by taking a long-term perspective and carrying out proper forestry operations as needed. Appropriate forest management and operations enable forests to provide public benefits, carbon credits, and useable forest resources. We have designated these as particularly important benefits and functions and carry out specific initiatives accordingly.
Sustainable Forest Model
One important forest management issue to be addressed is how to make a forest economically sustainable. We think the key is to maximize the various benefits and functions of forests through appropriate forest management and operations and then reinvest the profits generated back into forestry management. Through this unique approach that leverages our abilities as a general trading company, we will create a positive cycle. Our Sustainable Forest Model establishes and expands this positive cycle, making forest management sustainable, even for private sector companies. In addition to implementing this model through our company-owned forests, we are also offering Mitsui & Co.'s functions to other forest owners and managers in order to raise the sustainability of forest management and contribute to the realization of a decarbonized society.
Mitsui's Forests
(As of the end of March 2022)
| Hokkaido Prefecture |
Chambetsu | 779ha |
|---|---|---|
| Kitami | 19ha | |
| Tofutsu | 885ha | |
| Dainitofutsu | 163ha | |
| Urahoro | 2,554ha | |
| Shitakorobe | 402ha | |
| Hombetsu | 108ha | |
| Ishii | 308ha | |
| Saru | 5,769ha | |
| Niwan | 4,750ha | |
| Niwan-otsu | 990ha | |
| Hobetsu | 525ha | |
| Shimukappu | 154ha | |
| Soya | 1,960ha | |
| Esashi | 309ha | |
| Hamatombetsu | 370ha | |
| Shosambetsu | 1,094ha | |
| Haboro | 826ha | |
| Kotambetsu | 310ha | |
| Numata | 10,446ha | |
| Shiriuchi | 221ha | |
| Izumisawa | 287ha | |
| Ono | 680ha | |
| Esan | 1,161ha | |
| Moheji | 10ha | |
| Oe | 238ha | |
| Furubira | 126ha | |
| Tomari | 248ha | |
| Aomori Prefecture |
Owani | 154ha |
| Akita Prefecture |
Babame | 100ha |
| Okurasawa | 39ha | |
| Akita | 49ha | |
| Yamagata Prefecture |
Kaname | 699ha |
| Fukushima Prefecture |
Tashiro | 999ha |
| Niigata Prefecture |
Koesawa | 53ha |
| Kanamaru | 405ha | |
| Yatsuguchi | 225ha | |
| Onnado | 5ha | |
| Nanba | 244ha |
| Toyama Prefecture |
Kawaranami | 81ha |
|---|---|---|
| Fukui Prefecture |
Kono | 26ha |
| Kidani | 515ha | |
| Chiba Prefecture |
Kameyama | 47ha |
| Gifu Prefecture |
Shirakawa | 112ha |
| Yakambata | 112ha | |
| Kanayama | 843ha | |
| Shizuoka Prefecture |
Omine | 56ha |
| Hirasawa | 72ha | |
| Aichi Prefecture |
Higashisonome | 109ha |
| Ushiroyama | 101ha | |
| Nagano Prefecture |
Kizawa | 137ha |
| Mie Prefecture |
Sando | 1,138ha |
| Takaodani | 45ha | |
| Iga | 56ha | |
| Suzuka | 142ha | |
| Shima | 73ha | |
| Ikusei | 14ha | |
| Wakayama Prefecture |
Samoto | 202ha |
| Kainogawa | 99ha | |
| Miyama | 129ha | |
| Toura | 155ha | |
| Kokuoyama | 290ha | |
| Hyogo Prefecture |
Sekinomiya | 30ha |
| Nara Prefecture |
Takahara | 106ha |
| Tonokawa | 16ha | |
| Tenkawa | 67ha | |
| Nosegawa | 110ha | |
| Kyoto Prefecture |
Kiyotaki | 189ha |
| Hiroshima Prefecture |
Kimita | 164ha |
| Yamaguchi Prefecture |
Ogasa | 15ha |
| Nishiki | 254ha | |
| Oita Prefecture |
Jogatake | 179ha |
| Tsukinoki | 41ha | |
| Kumamoto Prefecture |
Yabe | 14ha |
| Total | 74 locations | |
| Total area | 444 km2 (44,403ha) |
|
Types of Trees Cultivated in Our Forests
Forests for Regeneration and Harvest
.jpg)
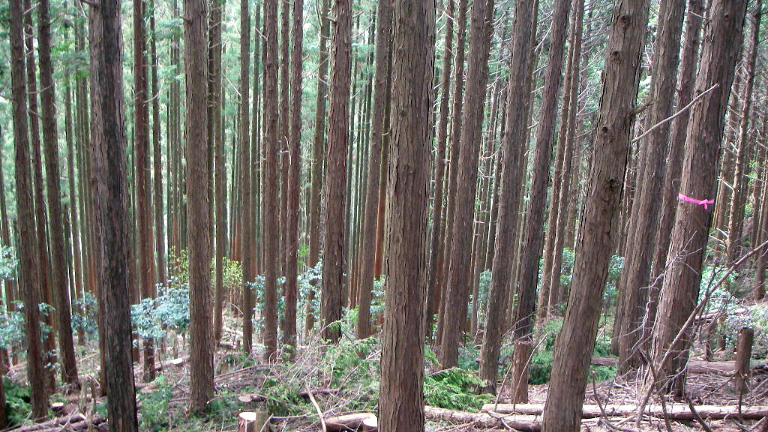
Japanese Cedar
- Characteristics
- A tall evergreen tree found widely throughout Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. Peculiar to Japan, it grows naturally in various environments including in mountainous areas, on marshland borders, and on rocky substrates. It is widely used for plantation. Trees grow to a height of 20 to 30 meters and a diameter of 60 to 100 cm and are characterized by a straight trunk, long under-branch height, and slender branches.
- Applications
- Building materials, architectural fittings, furniture, plywood

Japanese Cypress
- Characteristics
- Found in Honshu from Fukushima Prefecture southward and in Shikoku and Kyushu, this tall evergreen tree reaches a height of 30 meters and a diameter of one meter or more. It is characterized by a straight trunk, long under-branch height, and slender branches. The timber has a distinctive fragrance and sheen. Grows more slowly than the Japanese cedar, but thrives even in dry conditions.
- Applications
- Building materials, temple and shrine buildings, architectural fittings, furniture, wood carvings
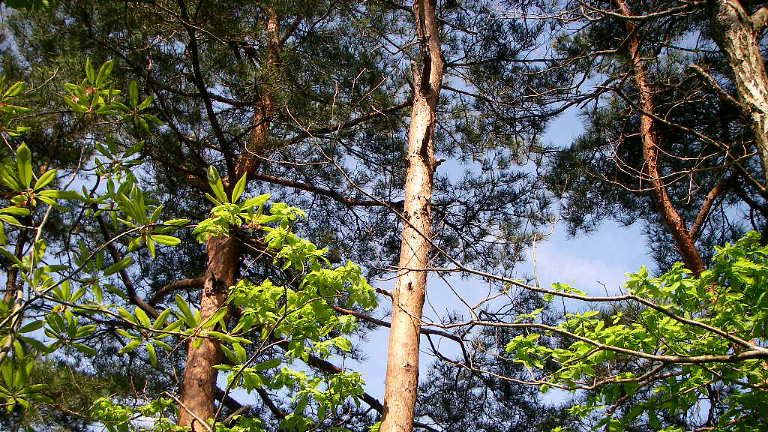

Japanese Red Pine
- Characteristics
- Tall evergreen tree found in southern Hokkaido and in Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. Reaches a height of 20 to 30 meters, a diameter of 50 to 150 cm, and has reddish-brown bark. Grows well even in dry conditions and poor soil and is noted for favoring the growth of the prized matsutake mushroom in its vicinity.
- Applications
- Structural beams and piles, civil engineering, packaging materials, pulp

Japanese Larch
- Characteristics
- Japan's only naturally native deciduous conifer, grows to a height of 20 to 30 meters and a diameter of 60 to 80 cm. Favors airy and well-drained locations. Has been used for plantations extensively in various regions, including Hokkaido, where it shows the strongest growth of any of the coniferous tree species used for afforestation. Naturally regenerating Japanese larch is found in Honshu from Miyagi Prefecture and Niigata Prefecture southward into the Chubu mountain region.
- Applications
- Building materials, plywood, furniture, packaging materials, pulp

Sakhalin Fir
- Characteristics
- Tall evergreen conifer found in Hokkaido and reaching a height of 20 to 25 meters and a diameter of 50 to 70 cm. Favors adequately moist and rich soils. Upward growth is somewhat slow when immature, but shows prolific growth from 10 or 20 years to around 40 years of age.
- Applications
- Plywood, architectural fittings, civil engineering, packaging materials. Makes excellent pulp.

Glehn's Spruce
- Characteristics
- Evergreen conifer found Hokkaido, grows to a height of 20 to 40 meters and a diameter of 50 to 80 cm; under favorable conditions it can reach a height of 40 meters and a diameter of 1.5 meters. The timber is rather soft and therefore easy to work.
- Applications
- Building materials, musical instruments
*Reference material: modern forestry dictionary; illustrations identifying trees by leaves, blossom, and bark.
Characteristics (Mar 31, 2019)
Trees Growing in Forest for Regeneration and Harvest
Tree Age
Natural Forests and Naturally Regenerated Forests (broad-leaved)

Monarch Birch
- Characteristics
- Found in the temperate zone from Hokkaido to northern Honshu in rich soil and sunny positions. As the bark is rich in oil and burns well, it is used to make torches for traditional events, for instance cormorant fishing displays.
- Applications
- High-quality furniture, architectural interior fittings

Japanese Oak
- Characteristics
- Found throughout Japan as far south as Kagoshima Prefecture and reaching a height of 30 meters and a diameter of 1.5 meters, this large deciduous tree has a majestic stature. When felled, large amounts of moisture are found in the timber, which is the origin of its Japanese name mizunara ('water oak'). Has been exported to America and Europe since the early 20th century for use as cut lumber.
- Applications
- High-quality furniture, architectural interior fittings, barrels

Japanese Elm
- Characteristics
- A large tree found growing naturally across a wide area including Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Tsushima, reaching 30 meters in height and one meter in diameter, and forming a round crown with the spread of its thick branches. Characteristic is the slimy feel of the bark when stripped.
- Applications
- Furniture, utensils, musical instruments

Manchurian Elm
- Characteristics
- Found widely from Hokkaido to Kyushu in mixed stands with Japanese elm. Does not grow as large as the Japanese elm, reaching around 25 meters in height and 70 cm in diameter, but the quality and uses of the timber are very similar. Because of the strength of its bark, the Ainu people used its fibers to make cloth, rope, and other items.
- Applications
- Utensils (including Buddhist altar fittings), furniture, musical instruments

Katsura
- Characteristics
- Found widely from Hokkaido to Kyushu. Reaches as much as 30 meters in height and 2 meters in diameter. Specimens throughout Japan have been designated as protected natural monuments and some have been regarded as sacred. Despite the large girth, it suffers few flaws and little warpage and can provide large timbers, making it a very useful species.
- Applications
- Utensils (including Buddhist altar fittings), furniture, musical instruments

Japanese Beech
- Characteristics
- One of the commonest species in temperate forests, this tall deciduous tree is found from southwestern Hokkaido to as far south as Kagoshima Prefecture and reaches a height of 25 to 30 meters and a diameter of around 1.5 meters. The so-called inubuna (Fagus japonica) is a very similar species, and because the bark is blackish in color it is sometimes known as the shirobuna ('white beech').
- Applications
- Furniture, flooring

Prickly Castor Oil Tree
- Characteristics
- Found from Hokkaido south to Kyushu and is said to have been given its name because of the sharp spines on its branches. A tall deciduous tree, it can grow as large as 25 meters in height and 1 meter in diameter and has blackish-brown bark. The leaves, which grow 20 to 30 cm in both length and breadth, are said to resemble a "giant's fan".
- Applications
- Furniture, musical instruments

Japanese Ash
- Characteristics
- Small deciduous tree, found from Hokkaido to Yakushima and growing to around 5 meters tall, with even the largest specimens reaching only around 12 meters in height and 60 cm in diameter. As the timber is strong and tough, it is said to be best suited for sports equipment.
- Applications
- Baseball bats, tennis and badminton racquet frames

Manchurian Ash
- Characteristics
- Native to Hokkaido and in northern and central Honshu from Nagano Prefecture northward, this tall deciduous tree reaches a height of around 25 meters and a diameter of around one meter. Grows quickly with timber of good quality. As it also has a straight trunk, long under-branch height, and few flaws, it is relatively easy to work.
- Applications
- Western-style furniture, Japanese-style furniture

Horse Chestnut
- Characteristics
- Found widely from Hokkaido south to Kyushu and frequently in the Tohoku region, this is a large, deciduous tree which grows to a height of up to 30 meters and a diameter of sometimes more than 2 meters. The nuts contain a high level of starch and were an important food in Japanese prehistory.
- Applications
- Furniture, building materials, base material for lacquerware
*Reference materials: modern forestry dictionary; illustrations identifying trees by leaves, blossom, and bark; tree/wood dictionary.
Natural Forests and Naturally Regenerated Forests (coniferous)

Asunaro
- Characteristics
- Found in southern Hokkaido to as far south as Tochigi Prefecture and is particularly common in the Tsugaru and Shimokita Peninsula regions of Aomori Prefecture. A tree species peculiar to Japan, it is an evergreen conifer growing to 30 meters in height and 80 cm in diameter. The Aomori asunaro is said to be one of the three most beautiful forest trees in Japan, along with the Kiso cypress and the Akita cedar.
- Applications
- *The oil extracted from the tree is also used for medicinal purposes

Japanese Douglas Fir
- Characteristics
- The Douglas fir is represented by only one species in Japan, which has a very limited distribution, being found only in the southern part of the Kii peninsula and the Yanase region of Kochi Prefecture. A tall evergreen tree, this member of the pine family grows to 30 meters in height and one meter in diameter.
- Applications
- Building materials, civil engineering *Available only in very limited quantities
*Reference materials: modern forestry dictionary; illustrations identifying trees by leaves, blossom, and bark; tree/wood dictionary.












